C: int numt = pvm_spawn(char *task,char **argv,int flag,
char *where,int ntask,int *tids)
M: [numt,tids] = pvm_spawn(task,argv,flag,where,ntask)
The routine pvm_spawn starts ntask copies of the executable
file task on the virtual machine. argv is a cell array of strings
containing the arguments to the task (each cell one argument). If the task
takes no arguments then argv is an empty cell. The flag
argument is used to specify options, and is a sum of:
- 0 (PvmTaskDefault) PVM chooses where to spawn processes
- 1 (PvmTaskHost) the where argument specifies a
particular host to spawn on
- 2 (PvmTaskArch) the where argument specifies a
PVM_ARCH to spawn on
- 4 (PvmTaskDebug) starts these processes up under
debugger
- 8 (PvmTaskTrace) the PVM calls in these processes will
generate trace data
- 16 (PvmMppFront) starts process up on MPP front-end
- 32 (PvmHostCompl) starts process up on complement host
set
On return numt is set to the number of tasks successfully spawned
or an error code if no task could be started. If tasks were started, then
pvm_spawn returns a vector of the spawned tasks' tids and if
some tasks could not be started the corresponding error code are placed
in the last (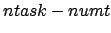 ) positions of the vector.
) positions of the vector.
pvm_spawn returns immediately after spawning the tasks.
Rene Fink
2006-04-24